Medicare and Hearing Aids: What Seniors Need to Know
If you’re a senior considering hearing aids, one of the biggest questions is likely about cost and insurance coverage. “Does Medicare cover hearing aids?” is one of the most common inquiries we hear at Elderly Care First, and understanding the answer is crucial for planning and budgeting.
Navigating Medicare coverage can be confusing, especially regarding hearing health, which is often treated differently than general medical care. This guide provides clear, accurate information (based on current understanding for 2025 – always verify details for your specific situation) to help seniors and caregivers understand how Medicare parts relate to hearing aid costs.
Disclaimer: Medicare rules and plan benefits can change. The information provided here is for general informational purposes based on publicly available information. Always verify coverage details directly with Medicare or your specific Medicare plan provider.
Original Medicare (Part A and Part B): The General Rule
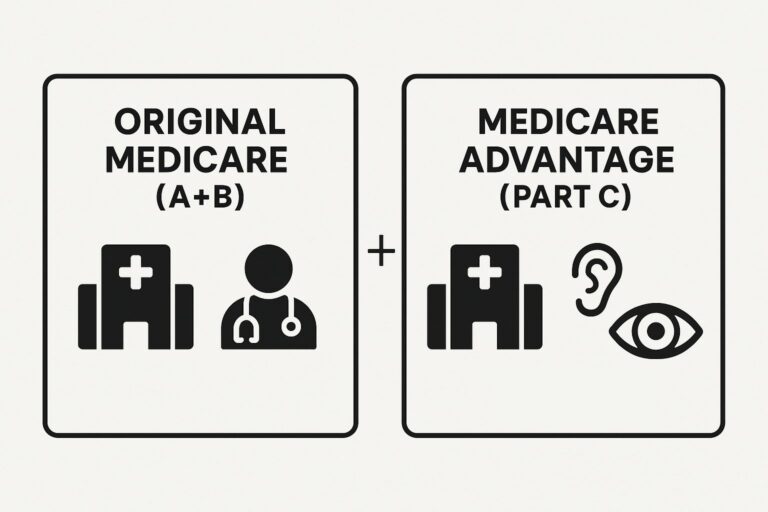
Let’s start with the basics: Original Medicare (Part A hospital insurance and Part B medical insurance) generally does NOT cover:
- Hearing aids themselves.
- Exams specifically for fitting hearing aids.
- Routine hearing tests.
This often comes as a surprise and can be a significant financial hurdle for many seniors needing hearing assistance, as hearing aids can be a major expense.
What Medicare Part B Might Cover (Diagnostic Tests)
While Original Medicare doesn’t cover hearing aids or routine tests, Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance) MAY cover diagnostic hearing and balance exams IF your doctor or other qualified healthcare provider orders them as medically necessary to determine an underlying medical condition.
For example, if you experience sudden hearing loss or dizziness, your doctor might order tests to diagnose the cause (like an infection, Meniere’s disease, or another condition requiring medical treatment). In such specific cases, where the test is part of diagnosing or treating a medical problem (not just fitting a hearing aid), Part B might cover 80% of the Medicare-approved amount after you meet the Part B deductible.
Key Point: Coverage is for diagnostic purposes ordered by a doctor for a medical reason, not for routine hearing checks or exams solely for the purpose of getting hearing aids. Always confirm coverage specifics beforehand. Medicare.gov – Hearing Exams
Medicare Advantage Plans (Part C): Where Coverage Often Differs
This is where the answer becomes more complex and often more hopeful for seniors seeking hearing aid coverage. Medicare Advantage Plans (Part C) are offered by private insurance companies approved by Medicare. These plans must cover everything Original Medicare covers, but they often include additional benefits, which frequently include:
- Hearing Exams: Coverage for routine hearing tests.
- Hearing Aids: Partial or full coverage for hearing aids, often through specific providers or with an allowance (a set dollar amount towards the cost).
- Fittings and Adjustments: Coverage for services related to fitting the hearing aids.
Crucially, the level of hearing benefit varies GREATLY from one Medicare Advantage plan to another. Some plans might offer a generous allowance, while others might cover only basic models or require significant copayments. Coverage might also be limited to specific brands or providers within the plan’s network.
If you have a Medicare Advantage plan or are considering one:
- Check Your Specific Plan Documents: Carefully review your plan’s Evidence of Coverage (EOC) or contact the plan provider directly. Look for sections on hearing benefits, hearing aids, and any associated costs (copays, coinsurance, deductibles, annual limits, network restrictions).
- Ask Specific Questions: Don’t assume coverage. Ask your plan provider:
- Is there a benefit for hearing aids?
- What is the allowance amount or coverage percentage?
- Do I need to use specific providers or brands?
- Are hearing exams and fittings covered?
- Are there any deductibles or copays I need to pay?
Other Potential Options for Help with Hearing Aid Costs

If Medicare (Original or Advantage) doesn’t cover your needs, or if costs remain high, consider these possibilities:
- Veterans Affairs (VA) Benefits: Eligible veterans may receive hearing aids and related services through the VA healthcare system.
- Federal Employee Health Benefits (FEHB) Program: Some FEHB plans offer hearing aid benefits.
- Private Insurance: If you have separate private health insurance (e.g., through a former employer), check if it includes hearing aid coverage.
- State Programs & Vocational Rehabilitation: Some state-specific programs or vocational rehabilitation services might offer assistance. Check your state’s Department of Health or Aging website.
- Non-Profit Organizations & Charities: Organizations like the Lions Club or Sertoma may offer assistance programs for hearing aids on a local level.
- Financing Options: Many audiologists and hearing aid retailers offer payment plans or financing options.
- Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) or Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): If you have one of these accounts, funds can typically be used for hearing aids and related expenses.
- Over-the-Counter (OTC) Hearing Aids: For adults with perceived mild-to-moderate hearing loss, FDA-approved OTC hearing aids are available without a prescription and are generally less expensive than traditional prescription aids.
OTC Hearing Aid Guide (coming soon)
Conclusion: Check Your Specific Coverage Carefully

To summarize:
- Original Medicare (Part A & B): Generally does NOT cover hearing aids or routine exams for fitting them. May cover diagnostic tests if medically necessary.
- Medicare Advantage (Part C): Often DOES include hearing aid benefits, but coverage varies widely by plan. You MUST check your specific plan details.
- Other Options: Explore VA benefits, private insurance, state programs, non-profits, financing, FSAs/HSAs, and OTC hearing aids.
Understanding your specific insurance coverage is the first step in planning for hearing aids. Don’t hesitate to contact Medicare or your plan provider directly to get clear answers about your benefits.
Elderly Care First is dedicated to helping you navigate these important health decisions. Explore our hearing health resources for more information. Ear Care